✍️ CRR Cash Reserve Ratio is the minimum fraction of total deposits of a bank’s customers that banks have to hold as reserves with the central bank. ✍️ SLR Statutory Liquidity Ratio is the ratio of liquid assets to the net demand and time liabilities. ✍️ LAF Liquid Adjustment Facility is a tool to allow banks to borrow money through repurchase agreements. It consists of repo and reverse repo operations. ✍️ MSF Marginal Standing Facility allows scheduled banks to borrow funds overnight from RBI against approved government securities. ✍️ MSS Market Stabilization Scheme is a monetary policy intervention by RBI to withdraw excess liquidity by selling government securities in the economy. ✍️ OMO Open Market Operations refers to the buying and selling of government securities in the open market so as to expand or contract the amount of money in the banking system. ✍️ REPO Repo...
The Mauryan Empire started from Magadha was founded in 321 BC by Chandragupta Maurya. Mudrarakshasha written by Vishakadatta beautifully summarizes the rise of Chandragupta Maurya with the help of Chanakya. Chandragupta Maurya patronized Jainism.
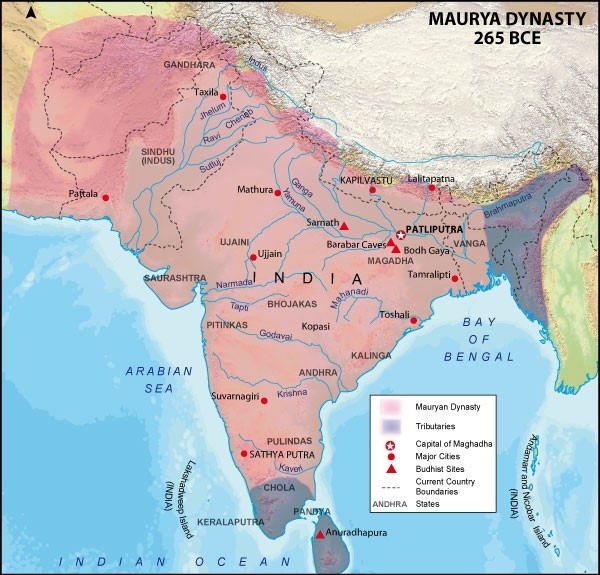
Pataliputra, modern-day Patna was the capital city of Mauryan Empire.
Expansion of Mauryan Empire:-
Mauryan Empire was one of the world's largest empires of that time and expanded to an area of 5,000,000 km2. Leaving the parts of NE India, Kerala and Tamil Nadu, the Mauryans ruled over the rest of Indian Subcontinent.
Imperial Organization
Accounts of Megasthenes in his book Indika and the Arthashastra (written by Kautilya) describe the elaborate arrangements made in the Mauryan administration, society and economy.
The empire was divided into provinces which were under Princes. Along with this, a dozen departments, the armed forces containing six wings were also maintained. Chandragupta established a well-organized administrative system and gave it a sound financial base.
Bindusara (298-273 BC)
He was known to Greeks as Amitrochates and he patronized the Ajivika sect.
Ashoka:
Ashoka ascended the throne in 273BC and ruled up to 232 BC. He was known as ‘Devanampriya Priyadarsi’ the beautiful one who was the beloved of Gods.
Ashoka fought the Kalinga war in 261 BC. Kalinga is in modern Orissa.
Ashokan inscriptions were deciphered by James Princep.
After the battle of Kalinga, Ashoka became a Buddhist, being shocked by the horrors of the war, he replaced Bherighosha by Dhammaghosha
Ashoka was initiated to Buddhism by Upagupta or Nigrodha, a disciple of Buddha
For the propagation of Buddhism Ashoka started the institution of Dharmamahamatras.
Ashokan Inscriptions
Ashokan inscriptions carried royal orders through which he was able to speak directly to the people. There were rock edicts and pillar edicts which were again divided into major and minor.
The 14 Major Rock Edicts of Ashoka tell about the principles of Dharma
The Kalinga rock edict explains the principles of administration after Kalinga war. In his Kalinga edict, he mentions ‘‘All men are my children’’
The Major Rock Edict XII of Ashoka deals with the conquest of Kalinga.
The term ‘Ashoka’ was mentioned only in the Maski Minor rock edict.
Ashoka and Buddhism
Ashoka held the third Buddhist council at his capital Pataliputra in 250 BC under the presidentship of Moggaliputa Tissa.
He sent his son and daughter to Sri Lanka for the spread of Buddhism (Mahendra and Sanghamitra)
Ashoka spread Buddhism to SriLanka and Nepal. He is known as the Constantine of Buddhism.
Ceylon’s ruler Devanmpriya Tissa was Ashoka’s first convert to Buddhism.
The broad objective of Ashoka’s Dhamma policy was to preserve the social order.
Ashoka ruled for 40 years and died in 232 BC.
Mauryan Administration
Highly centralized administrative structure. Chanakya mentions the 7 elements of Saptanga theory in administration. The king is assisted by his Mantri Parishad. Important officials were appointed for various administrative activities.
The administration was divided in four units
The chakra or the province
The Ahar or the district
The Sangrahana or a group of villages
The Gram or village
The municipal administration headed by a Nagarak was also found in Arthashastra.
Mauryan Art
Royal Art – The Royal palaces, pillars, caves, stupas etc.
Popular art – Figure sculptures, Terracotta objects etc.
The emblem of the Indian Republic has been adopted from the four-lion capital of one of Ashokan pillars which is located in Sarnath. Another four-lion capital at Sanchi, Single lion capital at Rampurva and Lauria Nandangarh, single bull at Rampurva, carved elephant at Dhauli are found.
The Mauryas introduced Stone Masonry on large scale. They started the process of “hewing out” caves from rocks and construction of stupas to store the relics of Buddha and Bodhisattvas which in later stages were expanded by Guptas.
Reasons for the decline
Highly centralized Mauryan administration
Partition after the death of Ashoka disturbed the unity of the empire
Weak later Mauryan rulers were also a cause of the decline of the empire


Comments
Post a Comment