✍️ CRR Cash Reserve Ratio is the minimum fraction of total deposits of a bank’s customers that banks have to hold as reserves with the central bank. ✍️ SLR Statutory Liquidity Ratio is the ratio of liquid assets to the net demand and time liabilities. ✍️ LAF Liquid Adjustment Facility is a tool to allow banks to borrow money through repurchase agreements. It consists of repo and reverse repo operations. ✍️ MSF Marginal Standing Facility allows scheduled banks to borrow funds overnight from RBI against approved government securities. ✍️ MSS Market Stabilization Scheme is a monetary policy intervention by RBI to withdraw excess liquidity by selling government securities in the economy. ✍️ OMO Open Market Operations refers to the buying and selling of government securities in the open market so as to expand or contract the amount of money in the banking system. ✍️ REPO Repo...
The Rise and Growth of the Gupta Empire
Background
After the fall of Mauryan empire, the Kushans in the North and Satavahanas in the south had held power. Gupta empire replaced the Kushans in the North with its center of power at Prayag and gave politicial unity for more than a century (335AD-455AD). It was founded by Sri Gupta. Gupta strength laid in the use of horses and material advantage of fertile land and natural resources abundant region.
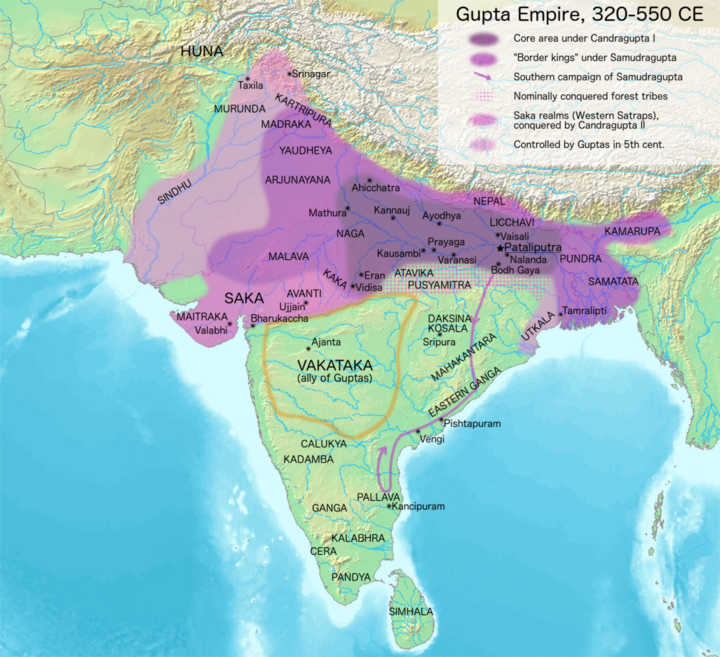
Chandragupta I (319-334 AD)
He was the first great ruler of Gupta Dynasty. He assumed the title Maharajadhiraja. Married Licchhavi princess
Started the Gupta Era by 319-20 AD
The original type of Gold coins Dinaras was issued.
Samudragupta (335-380 AD)
He followed a policy of violence and conquest which led to enlargement of Gupta empire
Harisena, his court poet, vividly mentions his military exploits in Allahabad inscriptions
He reached Kanchi in the south which was ruled by Pallavas
Meghavarman, the ruler of Srilanka, sent a missionary for permission to build a Buddhist temple at Gaya
Samudragupta is called as Napoleon of India
Chandragupta II (380-412 AD)
He adopted the title Vikramaditya
He conquered Malwa and Gujarat which provided him access to the sea which enabled trade and commerce. Ujjain was made as the second capital
His court was adorned by the Navaratnasincluding Kalidasa and Amarasimha.
His exploits are glorified in Iron Pillar at Qutub Minar
Chinese pilgrim Fa-Hsien (399-414AD) visited India during his period.
Life in Gupta Age
System of Administration
They adopted Pompous titles such as Paeamabhattaraka and Maharajaadhiraja
The administration was highly decentralizedwith feudal lords ruling over minor provinces
Civil and criminal laws were highly demarcated
Kumaramatyas were the most important officers. But Guptas lacked elaborate bureaucracy like Mauryas. These offices also became hereditary in nature.
Grant of fiscal and administrative concessions to priests was also in practice. Agrahara grants and Devagraha grants were practiced.
Trends in trade and agrarian economy
Guptas issued a large number of Gold coins which were called as Dinars
There was a decline in the long distance trade with Romans which led to lesser gold content in the Dinars.
Land grants made to the priests brought many virgin lands under cultivation
Social developments
Brahmana supremacy continued during Gupta period
The Huns came to be recognized as one of the 36 clans of the Rajputs
The position of Shudras improved as they were permitted to hear Ramayana, Mahabharata and Puranas
The number of untouchables, the Chandalas, increased
The position of women improved as they were permitted to hear Ramayana, Mahabharata and worship Krishna. But the first example of Satialso appears in the Gupta period.
State of Buddhism
Buddhism did not receive royal patronage in Gupta Period, still stupas and Viharas were constructed and Nalanda became a center for Buddhist learning
Origin and growth of Bhagavatism
Worship of Vishnu and Narayana merged to form Bhagavatism or Vaishnavism
It was marked by Bhakti (loving devotion) and Ahimsa
Religious teachings were mentioned in Bhagavadgita, Vishnu Purana and Vishnu Smriti
Idol worship became a common feature of Hinduism
Gupta rulers followed a principle of tolerance
Art: Gupta period is called Golden age of ancient India. Art was mostly inspired by Religions
Rock cut caves – Ajanta, Ellora and Bagh caves
Structural temples – Dashavatar temple of Deogarh, Laxman temple of Sirpur, Vishnu temple and Varah temple of Eran. The growth of Nagara style also enabled the development of temple architecture in India
Stupas – Dhammek stupa of Sarnath, Ratnagiri stupa of Orissa, Mirpur Khas in Sindh developed in this period.
Paintings – Ajanta paintings and Bagh caves paintings
Sculpture – the Bronze image of Buddha near Sultanganj, Sarnath and Mathura school flourished during this period which supports the growth of Mahayana Buddhism and Idol worship.
Images of Vishnu, Shiva and some other Hindu gods were also found.
Literature
Religious – Ramayana, Mahabharata, Vayu Purana etc were re-written. Dignaga and Buddhagosha were certain Buddhist literature written in this period
Secular
Mudrarakshasha by Vishakadatta
Malavikagnimitra, Vikramorvashiyam, AbhijanaShakuntalam – Dramas by Kalidasa
Ritusamhar, Megadoot, Raghuvamsam, Kumarasambhavam – Poetries by Kalidasa
Mricchakatika by Sudraka
Kamasutra by Vatsyayana
Panchatantra by Vishnu Sharma
Scientific
Aryabhatiya and Surya Siddhanta by Aryabhatta
Romaka Siddhanta
Mahabhaskarya and Laghubhaskarya by Bhaskara
Pancha Siddhanta, Vrihat Jataka, Vrihat Samhita by Vrahamihira
Fall of the empire
Huns invasion during the reign of Skandagupta and his successors greatly weakened his empire
Rule of Yashodharman dealt a severe blow to Gupta empire.
The rise of feudatories and Governors becoming independent led to the disintegration of Gupta empire. Loss of western India had crippled them economically.


Comments
Post a Comment